

In the final phase, called Termination, the starting material has been consumed, and the peroxide radicals, as well as other radicals decompose into secondary oxidation by-products such as esters, short chain fatty acids, polymers, alcohols, ketones and aldehydes. Also in this phase, the rate of peroxide radical formation will reach equilibrium with the rate of decomposition to form a bell-shaped curve. These reactions can proceed exponentially, if not controlled. In this part of the process, a chain reaction of high energy molecules, which are variations of free radicals and oxygen, are formed and can react with other fatty acids. Once the initial radicals have formed, the formation of other radicals proceeds rapidly in this second phase called Propagation. In the first phase, called Initiation, the formation of free radicals begins and accelerates. Therefore, the oxidation products depend on the time. Oxidation: a three-step processįat/oil oxidation is a three-step process (Initiation, Propagation and Termination). Pork and chicken fat demonstrate a higher degree of unsaturated fatty acids compared with beef fat and are therefore more prone for rancidity. Light and heat promote this reaction, which results in the generation of aldehydes and ketones – compounds which impart off-odors and flavors to food products. Oxidative rancidity results from the breakdown of unsaturated fatty acids in the presence of oxygen. Oxidation occurs when an oxygen ion replaces a hydrogen ion within a fatty acid molecule and higher numbers of double bonds within the fatty acid increase the possibility of autoxidation.
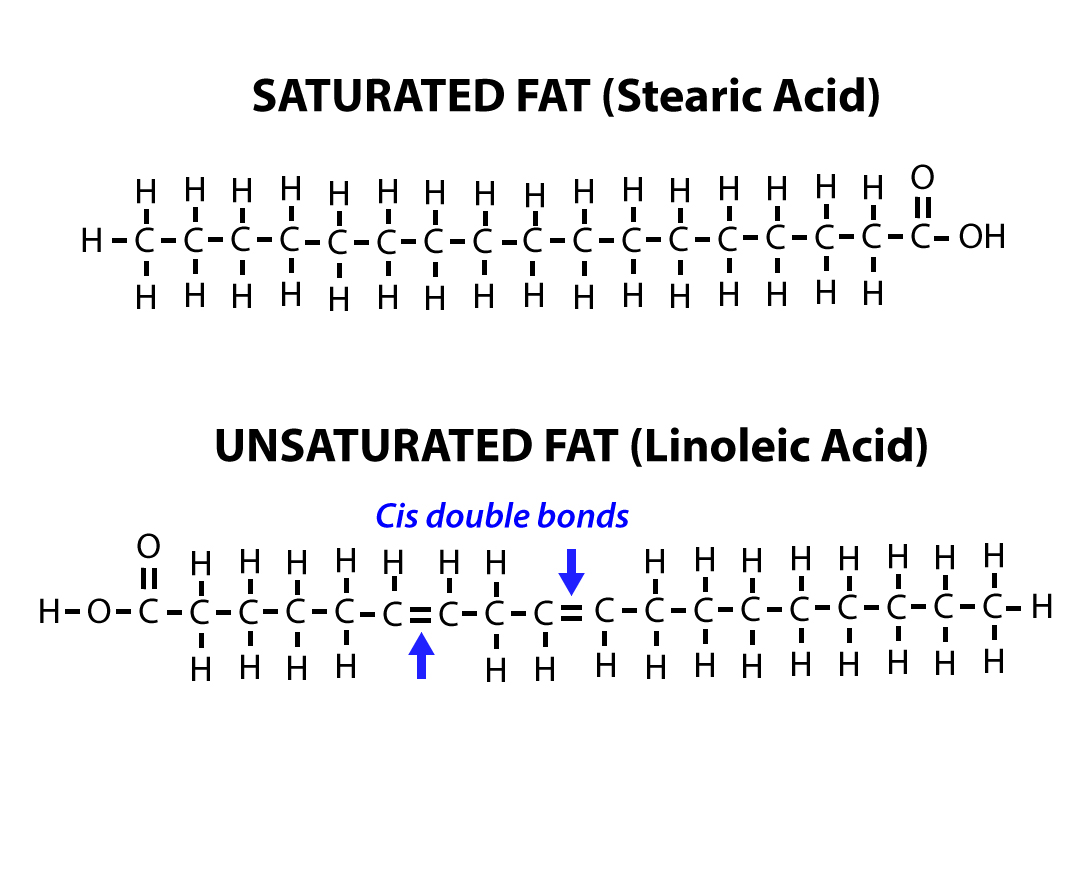
Fats are highly susceptible to degradation due to their chemical nature. Rancidity can occur naturally over time, but it can also be accelerated by improper storage or processing of animal products. This process is caused by the oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids and can be accelerated by factors such as exposure to light, heat, and air. Rancidity is the process by which fats and oils in food become degraded, resulting into off-odor/flavor, taste, and texture. It is conducted to determine the level of oxidation in samples of feed or feed ingredients and it can be performed through a number of analytical methods. Rancidity testing is essential in the feed industry, as a key indicator of product quality and shelf life. By Ajay Bhoyar, Global Technical Manager – Poultry, EW Nutrition


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
